Google Workspace has always prioritized data security, employing state-of-the-art cryptographic libraries to encrypt data both at rest and in transit. With the introduction of Client-Side Encryption (CSE), Google Workspace takes its encryption capabilities a notch higher, allowing customers to have sole possession of encryption keys and, therefore, have complete control over access to their data.
Fortanix Data Security Manager™ seamlessly connects into Google Workspace to deliver the additional layer of data protection and control. With Fortanix, Google Workspace admins and security professionals can externally manage keys and store them on a natively integrated FIPS 140-2 level 3-certified HSM, available as SaaS.
Related Read: Enhancing Data Privacy and Security in the Digital Age
They also benefit from centralized management with audit logging, enterprise-level access controls—RBAC and Quorum Approvals, and support for various interfaces, including REST APIs, PKCS11, CNG JCE, and KMIP. With Fortanix, teams now can elevate their data security and privacy to the next level to:
- Reduce impact of a data breach: In the event of a compromise to Google workspace, the data encrypted on the client-side remains secure as it is encrypted separately from Google's keys.
- Enhanced data privacy: sensitive customer data, critical business insights and intellectual properties are beyond the reach of prying eyes and unauthorized users.
- Data sovereignty: organizations can hold their encryption keys within a nation’s borders, or other defined boundaries.
- Improve compliance: adhere to data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPPA, ITAR, and more.
- Support crypto agility: rapidly migrate to quantum-proof cryptographic algorithms.
How Does Fortanix for Google Client-Side Encryption Work?
Google Workspace CSE works for browsers and mobile applications by encrypting and decrypting content on the end user’s devices. The Google Workspace client calls into Fortanix, which has been configured and deployed to provision keys to authenticated Google account users, and then the client performs cryptographic operations to seal and unseal Google Workspace content. Google Workspace CSE uses envelope encryption to protect data, and it relies on web browsers for performing client-side operations.
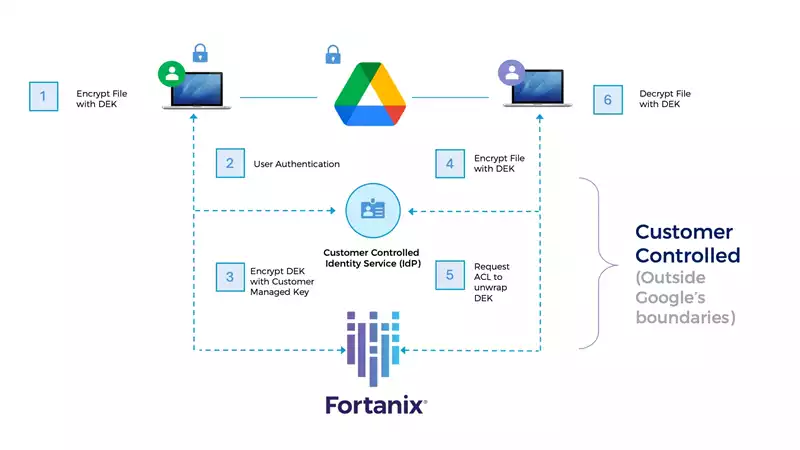
First, a data encryption key (DEK) is generated in a Google Workspace client, and it is used to encrypt the data symmetrically. Then the DEK is handed over to Fortanix DSM SaaS to be encrypted symmetrically using a Key Encryption Key (KEK). The encrypted content and the encrypted DEK are then sent to Google infrastructure for storage.
Want to give Fortanix a try?
You should-- with speedy deployment, you can be up and running in hours. You can learn more about Fortanix, and even start a free trial, at fortanix.com.











