Many organizations rely on Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) for data security to discover where sensitive data is located and what types of sensitive data are stored within the infrastructure.
DSPM security solutions quickly identify and categorize data assets based on risk level. This approach lets companies prioritize efforts and resources to secure their most sensitive and critical data first, followed by data not under the compliance radar.
DSPM offers a structured way to gain visibility into data holdings, but is DSPM enough?
DSPM can be a foundational component of a broader data security strategy, a baseline upon which further data security measures must be implemented and integrated. However, let's understand the next steps after DSPM implementation.
First, we briefly look into how DSPM security works, what is missing, and the fundamentals organizations often overlook.
DSPM: The First Step but Not the Last One
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) is a foundational data security strategy focusing primarily on data classification. It helps security teams identify which data needs to be secured first, allowing organizations to prioritize their security efforts.
For example, financial records, customer data, and intellectual property can be identified as high-risk assets requiring encryption to strengthen security and comply with regulations such as PCI-DSS.
Despite its useful data identification benefits, DSPM is not a cure-all for risks. It does not offer insights into how well the data is encrypted, how the keys are stored, and who has access to them.
The Missing Link in DSPM
To truly secure data, this is how organizations must look beyond DSPM. Specifically, they need to focus on three critical elements:
1) How Well Is Your Data Encrypted?
Encryption is the last line of defence in DSPM data security. It transforms readable data into an unreadable format that can only be decoded with a specific key. Also, not all encryption algorithms are created equal. For instance, AES-256 is highly secure, while older algorithms like DES are now outdated and vulnerable to be broken with computing power.
Consider a healthcare organization that stores patient records. They might use DSPM to classify these records as high-risk. However, the data remains vulnerable despite its classification if the organizations rely on outdated encryption methods. This is why the security teams must assess the quality of encryption continuously.
2) How Are Your Encryption Keys Managed?
Compromised encryption keys can make even the most securely encrypted data accessible to unauthorized parties. Encryption key management is not limited to generating and distributing keys but also securely storing them.
For example, a financial firm uses cloud-based services to store its encryption keys. If these keys are stored in plaintext or without adequate protection, they become an easy target for cybercriminals. Secure key storage solutions like Hardware Security Modules (HSM) or cloud-based key management such as Bring Your Own Key (BYOK services can mitigate this risk.
3) Who’s Accessing Your Encryption Keys?
Even with robust encryption and secure key storage, unauthorized user access can jeopardize data security efforts. DSPM doesn’t flag whether encryption keys are restricted to authorized personnel only or if non-privileged users, such as junior employees or contractors, also have access to these keys.
Organizations must monitor and control access to encryption keys. For example, a retail company might have multiple administrators with access to encryption keys. Without stringent access controls, any compromised account can lead to a data breach. Regular audits and access reviews are necessary to ensure that only authorized personnel have key access.
Role-based access controls, multi-factor authentication, and audit trails can help manage and track key usage.
Control Encryption Posture with Fortanix Key Insight
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) tools focus on discovering and classifying data but may not fully assess the effectiveness of encryption and key management practices.
This is why organizations need a centralized inventory and comprehensive assessment of their cryptographic assets.
This evaluation, offered by Fortanix Key Insight, helps identify gaps or weaknesses in data encryption by assessing critical details such as how encryption keys are stored if keys are rotated frequently, and if key access is not overly permissive. Without this, sensitive data might be exposed despite using DSPM, especially in complex environments like hybrid or multi-cloud setups.
How Does Fortanix Key Insight Work?
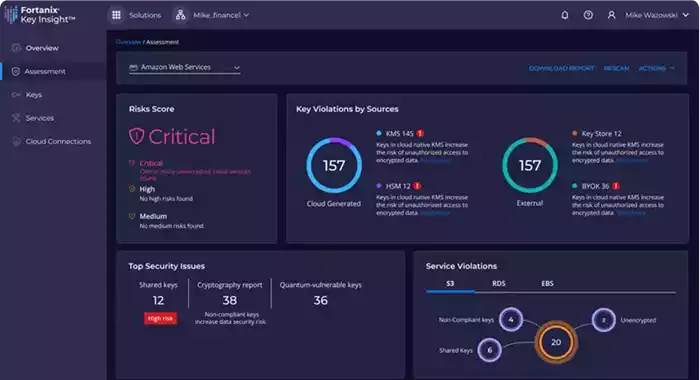
Fortanix Key Insight operates on three fundamental principles to enhance encryption key management and data security:
1. Discover Keys:
Fortanix Key Insight provides complete visibility into all encryption keys within your organization, and how they map to data services across on-premises and multicloud environments. This is especially important as organizations increasingly rely on multiple cloud providers, such as AWS or Microsoft Azure. Without visibility, encryption key sprawl increases the risk of data exposure. Fortanix offers a comprehensive, centralized visualization of all keys in use, making it easier for IT teams to manage and secure their data assets across different environments.
For example, if an encryption key used in AWS for a sensitive database is not tracked correctly, it could be left vulnerable to security breaches. Fortanix ensures all keys are easily located, monitored, and mapped to their respective services.
2. Assess Risk Posture:
Fortanix Key Insight evaluates an organization’s data security risks by analyzing key management best practices. For instance, regulations like PCI-DSS have strict encryption and key inventory requirements, and failing to comply can lead to costly penalties, breaches, and loss of business. Fortanix continuously assesses how your encryption keys align with these standards, identifying gaps or vulnerabilities. This ongoing assessment assists an organization to stay compliant and prepared for potential threats. For example, if a company’s encryption practices are outdated or fail to meet the latest regulatory changes, Fortanix will flag these risks and offer insights for remediation.
3. Remediate Issues:
When security risks or compliance issues are identified, Fortanix helps an organization take large-scale corrective actions to resolve them from a purpose-built data security platform. This includes automating tasks like rotating encryption keys, updating access policies, and implementing new encryption methods to meet your policies. This integrated remediation capability helps organizations strengthen their security posture without suffering from the complications of managing multiple-point solutions.
Conclusion
While DSPM provides a valuable starting point for data security, there are more complementary solutions to address a broad spectrum of data security risks. Organizations must also focus on the next step, i.e., Implementing Fortanix Key Insight to assess the effectiveness of data encryption and key management. By integrating Fortanix Key Insight, enterprises can ensure a more secure and compliant data environment.
Ready to take the next step in securing your data? Explore Fortanix Key Insight and discover how it can help reinforce your data security strategy.

 Cite this article
Cite this article









