If you're reading this in the morning, I hope you have your coffee handy, because the next five minutes are going to be quite exciting!
Let me ask you this, do you like reading the news? Alright, who really doesn't, especially if the news you listen is sassy and the talk of the town.
Every morning, I spend at least 30 minutes reading the latest cyber news. There is one thing that stays the same across all those "Breaking News" headlines, however. When I looked at them more closely, I saw that most of them have an obvious thing in common.
Let me see if you folks can figure this out on your own. Here are some of the most important data breaches that have been reported by online news outlets.
- Toyota Suffers Data Breach from “Mistakenly” Exposed Access Key on GitHub
- Uber hack linked to hardcoded secrets spotted in PowerShell script
- Rancher stored sensitive values in plaintext, exposed Kubernetes clusters to takeover
- Thousands of Secret Keys Found in Leaked Samsung Source Code
- Secrets in code combined with code leaks exposed data for 300,000 customers
So, folks, did you put the pieces together?
Yes, all of you cyber-savvy people who figured this out, I am talking about the most severe threat our industry is facing right now, which is exposing sensitive data in code, such as secrets, API keys, etc.
The number of cyberattacks is expected to be the highest ever in 2022. It was a busy year for people who work in cybersecurity all over the world.
Let me confess, as most people have probably done before: I was developing a script that makes a connection to a service with a username and password in order to get internal API calls from a CSP, and I simply placed the "secret" values right there in my source code. After all, only I can get to the data on my laptop, right? I will remember to hide these secrets if I ever have to give the script to someone else.
Well, sometimes we forget, or hackers get into our files on our laptops, and all of a sudden, we might have leaked information or secrets to public places that we shouldn't have. Sometimes we don't even realize that we've done this.
If you still don't believe me, how about I tell you about the worst security breach in the history of the world?
To put this in perspective, if you take into account the number of people in the world who have access to the internet, the proportion implicated in this breach climbs to 20.1% of the world's population that has access to the internet, which is far higher than the 12.9% of the global population that was affected by the breach based on current census statistics.
Of course, I'm referring about the latest Binance breach.
Many commentators have said things like "this is a wakeup call, we must take action" and "these are lessons learnt and we have to do better next time" in the aftermath of cyber-attacks. This is not a teachable moment or a call to action; rather, we are in the midst of a full-scale battle, and we have all fallen asleep at the wheel.
So, the burning question here is, what gave way to this?
Here, it all began when a developer accidentally posted a piece of stolen code on a blog on the Chinese Software Developer Networks (CSDN). The code snippet exposed the login information in clear text.
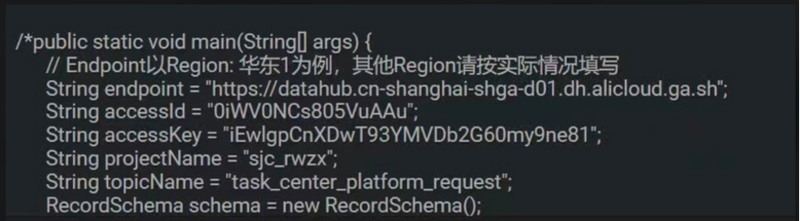
Code snippet containing a plain text secret
Once the secret was out in the open, attackers could exploit it to gain entry to privileged account regions and increase their privileges, giving them near-unrestricted access to the application landscape and the data inside it. An attacker inserts a malware that lives as an advanced persistent threat (APT) and silently monitored the system.
It turns out that secrets in code are the main reason why software supply chain security is broken. When secrets are left in the code, whether by accident or on purpose, hackers may use them to launch asynchronous attacks that can result in privilege escalation, vulnerability exploitation, and data exfiltration.
Secrets are just digital authentication credentials like OAuth tokens, API keys, certificates, passwords, and encryption keys that are used in services, infrastructure, and applications.
In the world of modern software, secrets are a MUST.
Development of open-source software has become the norm thanks to tools like GitHub. But there is a problem when this public code needs to handle authentication secrets like API keys or cryptographic secrets. For security reasons, these secrets must be kept secret. However, common development practises, like adding these secrets to code, make it easy for them to get out by accident.
Unfortunately, the fact that GitHub is public often goes against the need to keep login credentials secret. Because of this, these secrets are often made public by accident or on purpose as part of the repository. If source code gives away secrets, you, your team, and your whole company will be at risk. Any information about a business, person, or other thing that shouldn't be shared with the public. It could be a credit card number, a password, an access key, an API token, a certificate, a private key, or anything else.
Ignoring the risk that these long-forgotten secrets could be used by hackers in the future, which could have terrible results like we saw in case of previous breaches.
Did you know GitHub credentials may be hacked in 4 seconds?
To make matters worse, application security teams are well aware of this problem. But it takes a lot of work to look at, delete, and rotate the secrets that are kept each week or to search through years of unexplored areas.
Because of their importance and potential impact, secrets must be adequately safeguarded in any software architecture. Modern software development processes and the fact that source code, production logs, Docker images, and instant messaging apps are spread out make it hard to keep track of where they end up.
So, I'm not here to talk nonsensically about this problem while you all sip your coffee. Instead, I want to tell you about a "SECRET" way to solve these problems.
Now this isn't one of those things that has to be addressed in secret like the others we spoke about, but I could use your help getting the word out about this.
Like most cybersecurity problems, there are no quick solutions. Key Managers, on the other hand, have emerged as the tool of choice for enterprises looking to avoid permanently embedding credentials in their code. Secrets may be safely stored in a single location centrally thanks to such key managers.
Additionally, locking down the development environment to prevent public access, and putting up automatic code repository security and access checks, including scanning the internet for code snippets that may reveal source code leaking, are all necessary steps toward fixing these vulnerabilities.
Lastly, it is critical that businesses make cybersecurity a fundamental part of their corporate culture. It's still not simple, but it's far more doable if everyone knows why and how they require secure operations. Long-term security may be achieved by a layered defence strategy that includes policy, technological solutions like external encryption, key managers, and education to eliminate the possibility of passwords being accidentally left in source code.
Many of these kinds of attacks show how important it is to work with a security company like Fortanix. Fortanix is a data-first company and is redefining data security.
Fortanix Data Security Manager (DSM) SaaS offers integrated data security with encryption, multicloud key management, data tokenization, and other features, all of which are delivered as a service from a single platform.
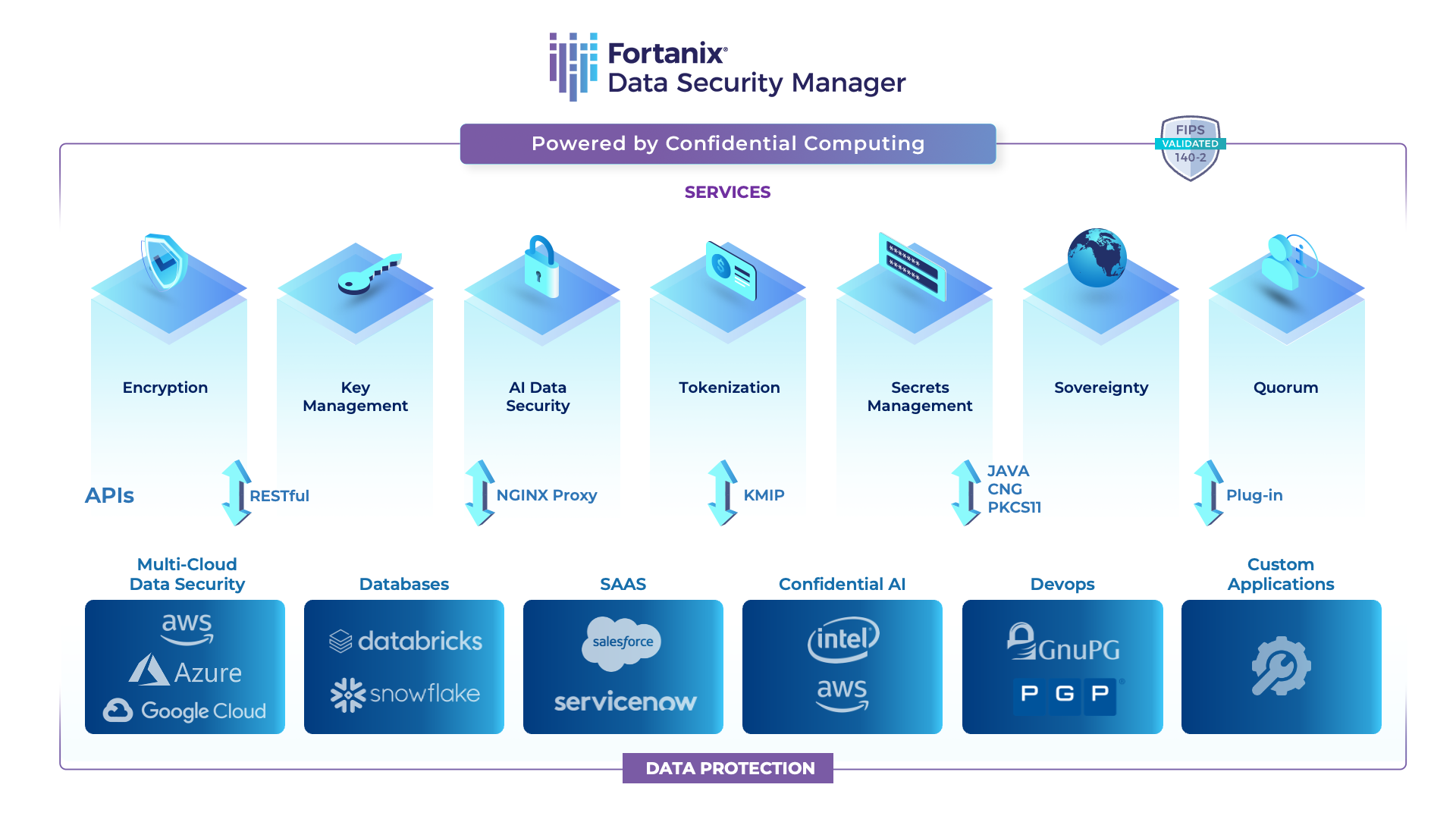
For every user. Any cloud. Anywhere in the world
So, I'd love it if you gave the DSM SaaS a try. You can set it up in five minutes while you drink your next cup of coffee, and the first 30 days are free.
I'm guessing you've finished your coffee by now, so let's end this post in a "Who Wants to Be a Millionaire?" style. Imagine you're in the hot seat and this last huddle is all that stands between you and the prize money.

So, do you agree? Please get in touch with me to discuss your ideas and receive your portion of the prize money 😊
Secrets management: Summary
The age of automation is just beginning, and information security goes hand in hand with end user privacy and business continuity.
We should be forewarned by the stream of attacks that often could be thwarted by simple practices that were established gradually over time at the core of the enterprise.
Application teams may find it easier to pilot a single service more securely in this manner rather than awaiting the information security leader or CISO to codify it within the enterprise.
The need for a proven secrets management application or service is ever present. Pick a solution that is:
Flexible in its deployment model whether on-premises or natively in the cloud, or some combination (hybrid, multi-cloud etc.)
Secure in a way that goes beyond a simple key-value store that most secrets management providers ultimately provide.
Capable of connecting to other applications and services through open standards such as OAuth, OpenID (SAML), LDAP, Trustworthy JWT and PKI
Proven to work for national agencies and regulatory bodies alike, since these entities have pivotal security considerations.
Conclusion
- Fortanix provides a single centralized platform to securely store, control and manage secrets outside the source code in a FIPS 140-2 level 3 certified HSM.
- With flexible deployment modes and scalable architecture, Fortanix secret management works across environments, on-premises, natively in the cloud, hybrid and multicloud.
- Integrates with any DevOps environment with Rest APIs.

 Cite this article
Cite this article








