The data driven world of finance
How financial firms handle, and store finances and data are a far cry from what it used to be about a decade back. For example, in today’s competitive world banks need to be more data-driven than ever before. This is critical to acquire more customers and deliver the best experiences.
“Data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to acquire customers, six times as likely to retain those customers, and 19 times as likely to be profitable as a result.”
– Forbes
Becoming nimble, accelerating revenues, and improving customer experiences have been the primary drivers for financial firms to implement digital transformation projects. But increased adoption of cloud, IoT, mobile applications etc. has led to an exponential growth of data.
Financial firms today sit on a mountain of data that’s not only constantly growing and but is also of the highest value. Its therefore not surprising why financial data is the most susceptible to cyberattacks.
Financial sector: The favorite playground of a hacker
Every cybercriminal out there seems to be picking on financial firms. As per the recent Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, the financial sector continues to be a favorite playground for hackers and cybercriminals. The data breaches in this sector are largely perpetrated by
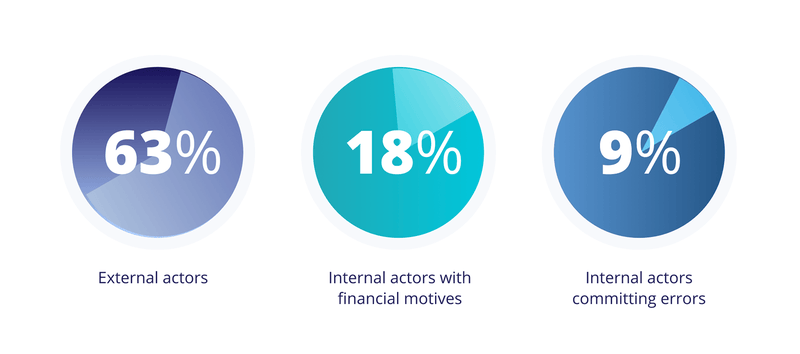
Of the 3,950 confirmed breaches reported, nearly 448 breaches are within the financial sector.
Another research report by BAE Systems Applied Intelligence, the cyber and intelligence arm of BAE Systems points out that 74% of financial institutions experienced significant rise in cybersecurity threats linked to COVID-19.

Quoting from the report, “A quarter of consumers also believe their Financial Institution (FIs) could do a lot more to protect them from cybercrime and over half now think it’s the job of FIs to do so - more so than the government, the police or themselves.”
With increasing incidents of data breaches being reported, the financial industry comes under more intensive scrutiny from government regulators and authorities concerned. They are subject to regulations that can drastically vary between countries and markets.
For example: there are regulations like PCI DSS for credit card data, GDPR for EU data across the globe, GLBA, SOX, and other different laws across the world. As these organizations scale, it is critical to ensure that the sensitive data is protected and meets these compliance requirements.
Snapshot of some important compliance regulations for financial services
| Compliance Standard | What is it about? | What is required? |
|---|---|---|
| The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) | Passed in 2002, by the United States Congress, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) was designed to improve the accuracy of corporate disclosures. Section 302 and 304 of the Act set standards for data protection. | -SOX does not specify any specific controls to protect the financial data, but encryption is mostly considered as the best practice. |
| Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) | The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act requires financial institutions that offer consumers financial products or services like loans, financial or investment advice, or insurance to explain their information-sharing practices to their customers and to safeguard sensitive data. | -Section 501(b) of the GLBA states that financial institutions must take the necessary measures to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of non-public customer information. |
| Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) | PCI DSS defines the operational and technical requirements for organizations accepting or processing payment transactions, and for software developers and manufacturers of applications/devices used in those transactions. | Encryption and tokenization is one of the key requirements of PCI-DSS. |
| EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is designed to provide better privacy and security to European citizens data and came into effect on May 25th, 2018. | Article 32 of the GDPR includes encryption as an example of an appropriate technical measure, depending on the nature and risks of your processing activities and is strongly encouraged. |
According to Gartner, “Privacy and data breaches continue to be widespread due to lack of data security governance and operational frameworks for encryption.”
Best practices for maintaining compliance and data security for financial organizations
Encryption key management or cryptography is often considered the most important security control to meet compliance standards. Here are the top five cryptographic practices that can help your financial firm comply with these regulations.
-
Adopt a data security approach that is cloud-scale and pervasive in nature. Today, cryptography is often underutilized, misconfigured, and siloed between different environments and groups within an organization.
To build digital trust, accelerate digital transformation, and minimize the risk of data breaches, it is critical that businesses use an agile encryption approach that standardizes and centralizes cryptographic operations so that encryption becomes pervasive throughout all applications, infrastructure, and digital business. -
Get exclusive control over your data with Bring Your Own Key Management System (BYOKMS). BYOKMS provides organizations with exclusive control over who can see and access the cloud data.
This is very important as it allows organizations to safely migrate applications to the public cloud and comply with regulations such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). In the shared infrastructure of the public cloud environments, BYOKMS can significantly reduce violation and misuse of keys including by cloud insiders and authorities. -
Store data encryption keys within a FIPS 140-2 level 3 certified Hardware Security Module (HSM). Banking and financial services data is best protected if the encryption keys are stored in FIPS 140-2 Level 3 validated HSMs. FIPS 140-2 Level 3 adds requirements for physical tamper-resistance (making it difficult for attackers to gain access to sensitive information contained in the module) and identity-based authentication.
FIPS 140-2 is the benchmark for the effectiveness, robustness, and tamper-proof resistance of your HSM/KMS. Level 3 certification is widely considered as the most advanced certification for an effective cryptographic system. -
Enforce extensive logging and auditing of data and access across your infrastructure. Ability to track encryption key information such as creation date, key rotations, expiry etc., or in short, the complete history of the key through the key management portal or REST API can provide you with greater visibility of data usage. All access to personal data needs to be automatically logged into a centrally viewable tamper-proof global audit trail to never have any dispute about who accessed which data and when.
-
Lock down your data with Confidential Computing and prevent financial fraud. With financial organizations facing a never-ending onslaught of digital fraud and theft, more and more customers are demanding the highest levels of security for their most critical cloud data. Confidential Computing is a new technology that allows organizations to unlock the value of their most private data while keeping it more safe and secure.
Organizations can now protect data and applications in use by running them within secure enclaves. With more and more use of data analytics within financial services, the technology can also be used for privacy preserving analytics within a secure environment. Some of the best use cases would be to employ the technology for AI-based money laundering detection utilizing federated learning, credit scoring, market rate calculations etc. Learn more about Confidential Computing.
And if your financial services firm is interested in implementing these practices to achieve compliance then reach out to us at sales@fortanix.com

 Cite this article
Cite this article







